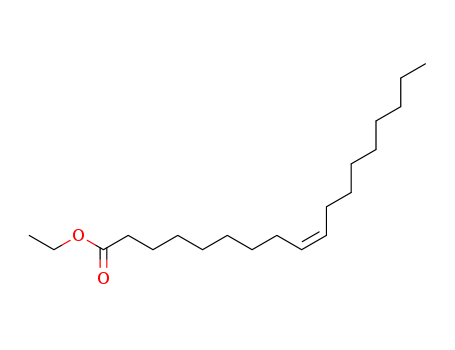

CasNo: 111-62-6
MF: C20H38O2
Appearance: clear pale yellow oily liquid
|
Overview |
Ethyl oleate is a colourless liquid that is normally formed by condensing ethanol and oleic acid. Notably, the compound is normally produced by the body during intoxication of ethanol. Its other names are 9-Octadecenoic acid (Z)-, Ethyl cis-9-octadecenoate, (Z)-9-Octadecenoic acid ethyl ester, and Oleic acid, ethyl ester. The compound contributed to approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine in porcine platelets. Ethyl oleate is neutral and is a more lipid-soluble form of oleic acid. The compound is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters that is generated after the breakdown of ethanol in the body. Moreover, ethyl oleate usually acts as a toxic mediator of ethanol in the heart, liver, pancreas, and brain. |
|
Production Methods |
Ethyl oleate is prepared by the reaction of ethanol with oleoyl chloride in the presence of a suitable hydrogen chloride acceptor. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A long-chain fatty acid ethyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of oleic acid with the hydroxy group of ethanol. |
|
Preparation |
By direct esterification of oleic acid with ethyl alcohol in the presence of HCl at the boil; in the presence of Twitchell’s reagent or chlorosulfonic acid. |
|
Aroma threshold values |
Detection: 130 to 610 ppm |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Ethyl oleate is primarily used as a vehicle in certain parenteral preparations intended for intramuscular administration. It has also been used as a solvent for drugs formulated as biodegradable capsules for subdermal implantation) and in the preparation of microemulsions containing cyclosporinand norcantharidin. Microemulsion formulations containing ethyl oleate have also been proposed for topical and ocular delivery, and for liver targeting following parenteral administration. Ethyl oleate has been used in topical gel formulations, and in self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems for oral administration. Ethyl oleate is a suitable solvent for steroids and other lipophilic drugs. Its properties are similar to those of almond oil and peanut oil. However, it has the advantage that it is less viscous than fixed oils and is more rapidly absorbed by body tissues. Ethyl oleate has also been evaluated as a vehicle for subcutaneous injection. |
|
Safety |
Ethyl oleate is generally considered to be of low toxicity but ingestion should be avoided. Ethyl oleate has been found to cause minimal tissue irritation. No reports of intramuscular irritation during use have been recorded. |
|
Carcinogenicity |
Not listed by ACGIH, California Proposition 65, IARC, NTP, or OSHA. |
|
storage |
Ethyl oleate should be stored in a cool, dry place in a small, wellfilled, well-closed container, protected from light. When a partially filled container is used, the air should be replaced by nitrogen or another inert gas. Ethyl oleate oxidizes on exposure to air, resulting in an increase in the peroxide value. It remains clear at 5°C, but darkens in color on standing. Antioxidants are frequently used to extend the shelf life of ethyl oleate. Protection from oxidation for over 2 years has been achieved by storage in amber glass bottles with the addition of combinations of propyl gallate, butylated hydroxyanisole, butylated hydroxytoluene, and citric or ascorbic acid. A concentration of 0.03% w/v of a mixture of propyl gallate (37.5%), butylated hydroxytoluene (37.5%), and butylated hydroxyanisole (25%) was found to be the best antioxidant for ethyl oleate. Ethyl oleate may be sterilized by heating at 150°C for 1 hour. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Ethyl oleate dissolves certain types of rubber and causes others to swell. It may also react with oxidizing agents. |
|
Regulatory Status |
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (transdermal preparation). Included in parenteral (intramuscular injection) and nonparenteral (transdermal patches) medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. |
InChI:InChI=1/C20H38O2/c1-3-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20(21)22-4-2/h11-12H,3-10,13-19H2,1-2H3/b12-11+
Three hundred and fifty novel lipases an...
Methathesis of ethyl oleate, catalyzed b...
The fatty acid moiety of 2-monoacyl-sn-g...
Ammonium and cesium derivatives from H3P...
The immobilization of Candida antarctica...
The use of water-permeable membranes for...
A true convert: The carboxylesterase enz...
Kinetics of the title reactions has been...
Immobilization of enzymes is important t...
Esterification of free fatty acid (oleic...
A highly efficient transformation of veg...
The α-hydrophobic long chain-α-amino est...
10,11-Dioctyleicosane, a star-shaped hyd...
A novel nucleoside lipid derived from di...
Biodiesel is a mixture of fatty acid alk...
Sporopollenin exine capsules (SECs), der...
Palladium(II)-catalyzed meta-selective C...
A simple easily scalable one-pot route t...
Sustainability in chemistry heavily reli...
This study was carried out to covalently...
Raman spectroscopy with a fiber-optic pr...
Esterification of oleic acid was carried...
The present document describes compounds...
Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus is o...
The present document describes compounds...
The present invention relates to an este...
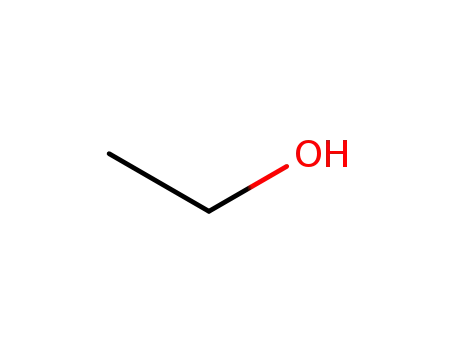
ethanol
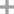
2-Oleodipalmitin

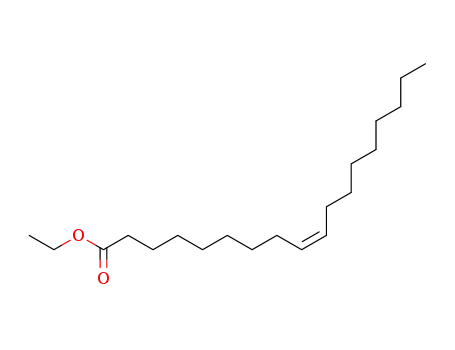
oleic acid ethyl ester

hexadecanoic acid ethyl ester

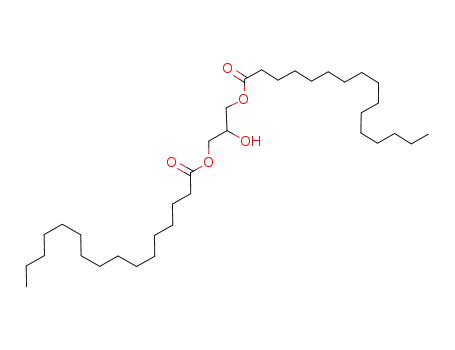
hexadecanoic acid, 2-hydroxy-1,3-propanediyl ester


1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-rac-glycerol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
immobilized EL1 lipase;
In
water; tert-butyl alcohol;
at 30 ℃;
for 4.16667h;
|
45 mmol 11 mmol |
fatty acids from sewage scum; extract of


ethanol

hydroxy fatty acid ethyl esters


oleic acid ethyl ester

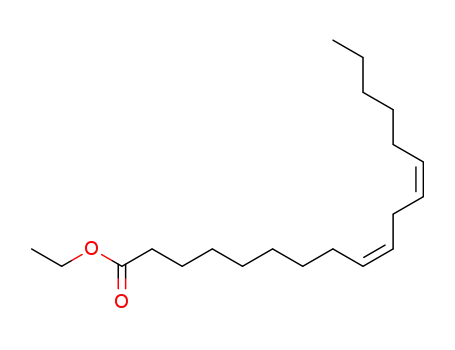
ethyl (9Z,12Z)-9,12-octadecadienoate

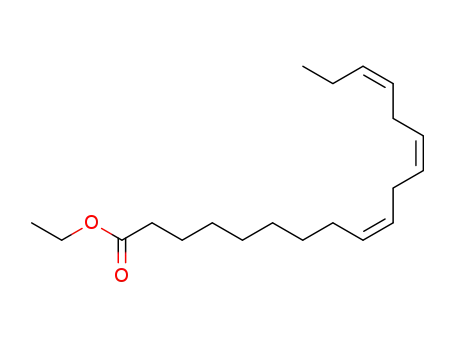
ethyl linolenate


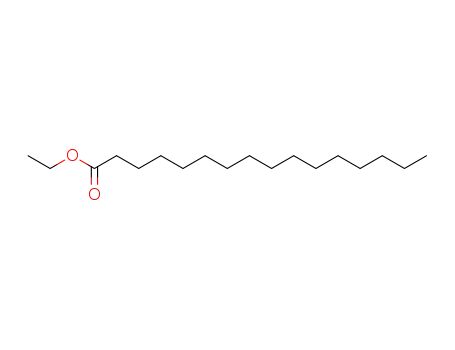
hexadecanoic acid ethyl ester

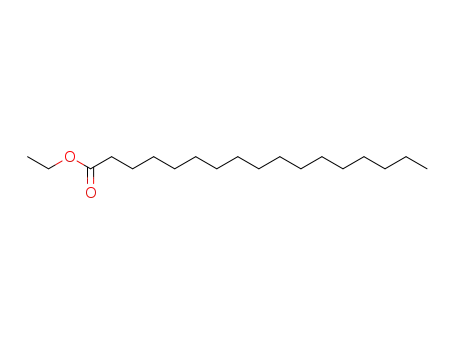
ethyl heptadecanoate

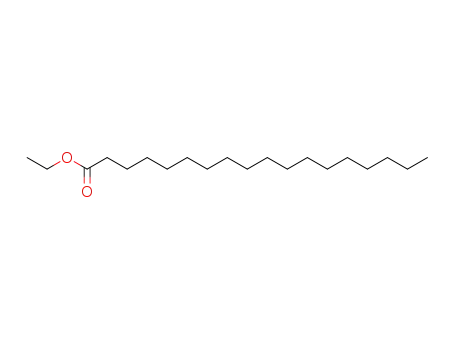
stearic acid ethyl ester
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
sulfuric acid;
at 60 ℃;
for 1h;
Conversion of starting material;
|

ethanol
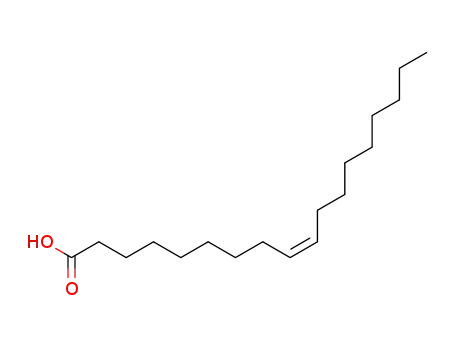
cis-Octadecenoic acid
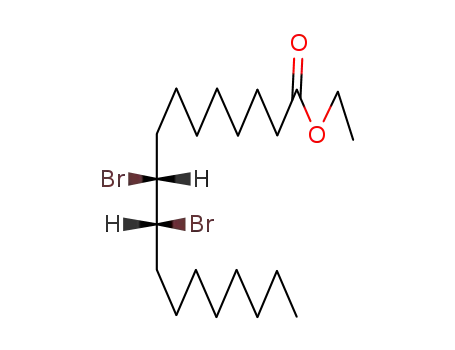
(+/-)-threo-9,10-dibromo-octadecanoic acid ethyl ester

potassium oleate
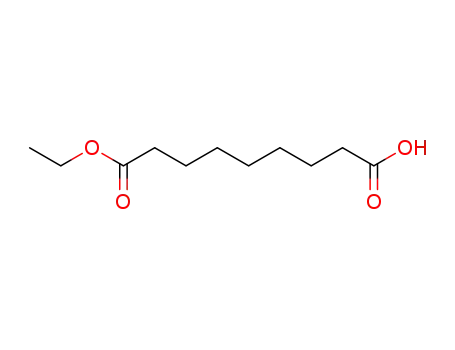
azelaic acid monoethyl ester
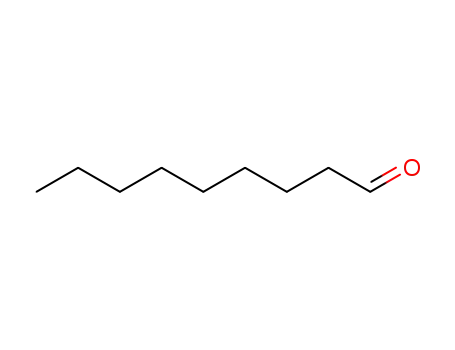
nonan-1-al
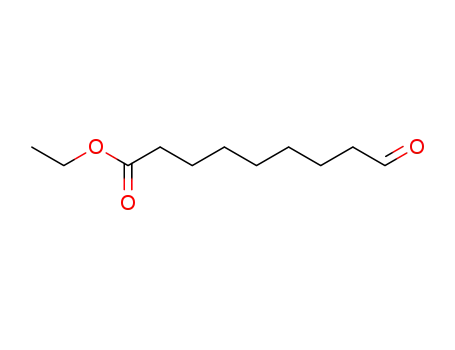
ethyl 9-oxononanoate

1-octadecanol