
CasNo: 813-94-5
MF: C12H10Ca3O14
Appearance: white powder or white to colourless crystals
|
Production Methods |
Calcium citrate is an intermediate in the isolation of citric acid from the fermentation process by which citric acid is produced industrially. The citric acid in the broth solution is neutralized by calcium hydroxide, precipitating insoluble calcium citrate. This is then filtered off from the rest of the broth and washed to give clean calcium citrate. The calcium citrate thus produced may be sold as-is, or it may be converted to citric acid using dilute sulfuric acid. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Calcium citrate is more easily absorbed (bioavailability is 2.5 times higher than calcium carbonate); it is easier to digest and less likely to cause constipation and gas than calcium carbonate. Calcium citrate can be taken without food and is more easily absorbed than calcium carbonate on an empty stomach. It is also believed that it contributes less to the formation of kidney stones. Calcium citrate consists of around 24% Ca2+, which means that 1000 mg calcium citrate contains around 240 mg Ca2+. The lower Ca2+ content together with the higher price makes it a more expensive treatment option compared to calcium carbonate, but its slightly different application field can justify this. |
|
Biological Activity |
In many individuals, bioavailability of calcium citrate is found to be equal to that of the cheaper calcium carbonate.However, alterations to the digestive tract may change how calcium is digested and absorbed. Unlike calcium carbonate, which is basic and neutralizes stomach acid, calcium citrate has no effect on stomach acid. Individuals who are sensitive to antacids or who have difficulty producing adequate stomach acid should choose calcium citrate over calcium carbonate for supplementation. According to recent research into calcium absorption after gastric bypass surgery , calcium citrate may have improved bioavailability over calcium carbonate in Rouxen- Y gastric bypass patients who are taking calcium citrate as a dietary supplement after surgery. This is mainly due to the changes related to where calcium absorption occurs in the digestive tract of these individuals. |
InChI:InChI=1/2C6H8O7.3Ca/c2*7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10;;;/h2*13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12);;;/q;;3*+2/p-6
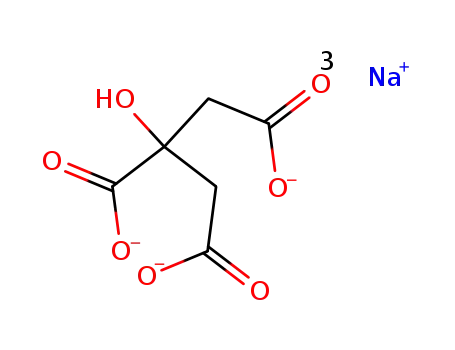
sodium citrate

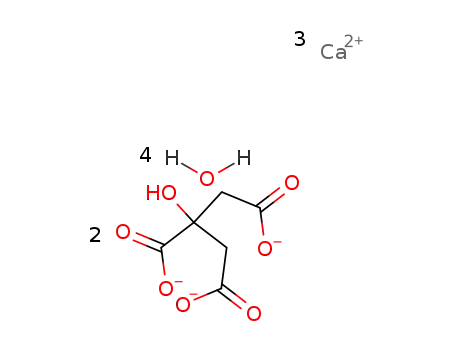
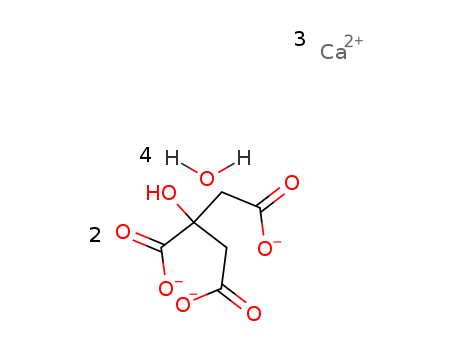
tricalcium citrate tetrahydrate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water;
|


tricalcium citrate tetrahydrate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Einfluss der Temperatur und der Konzentration auf die Bildung;
|

sodium citrate