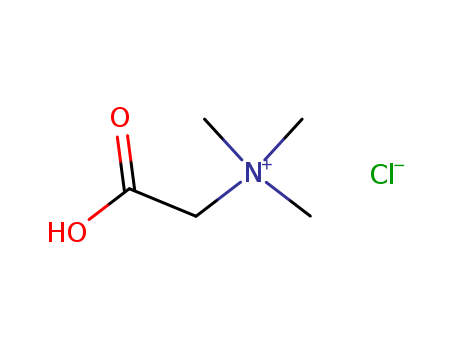

CasNo: 590-46-5
MF: C5H12ClNO2
Appearance: colorless to white crystals
|
Indications |
Betaine hydrochloride may be used as a lipotropic. Lipotropics aid in preventing the accumulation of fat in the liver, and usually help in the detoxification of metabolic wastes and toxins. They may be used to help with weight loss. Betaine hydrochloride has been used as a source of hydrochloric acid in the treatment of hypochlorhydria, a condition in which an abnormally low amount of hydrochloric acid is in the stomach. It has been used in preparations for the treatment of liver disorders, hypokalaemia (abnormally low levels of potassium in the blood), CO2 production in double contrast radiography, and high homocysteine. Betaine hydrochloride has also been used to treat tic douloreux (a condition which involves spasmodic pain along the course of a facial nerve), cystinuria (a hereditary defect that results in recurrent kidney stone formation), and vitiligo (a condition that is characterized by milky-white patches on otherwise normal skin). |
|
Biological Functions |
Betaine hydrochloride and pepsin are naturally occurring gastric-juice components that render nutrients available for absorption and biological acitivity. Specifically, Betaine hydrochloride is an acidic form of betaine, which promotes optimal gastric lumen acidity and pepsin is a protein-digesting enzyme that catalyzes the splitting of peptide bonds. Betaine HCl is an excellent source of hydrochloric acid, also known as stomach acid. Supplementing with betaine HCl can be very beneficial, as insufficient production of hydrochloric acid is fairly widespread and often overlooked. Certain situations, such as normal aging, can decrease the body’s natural production of HCl. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Betaine hydrochloride can decrease hepatotoxicity, that is stimulated by ethanol. |
|
Side effects |
Side effects are seldom seen, but as of 2013 betaine hydrochloride had not been through rigorous safety studies. Its safety, especially for young children, pregnant or nursing women, or those with severe liver or kidney disease, is not known. In very high doses, betaine hydrochlorine has been associated with heartburn or burning of the stomach lining. |
|
Drug interactions |
People taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), cortisone-like drugs, or other medications that could cause peptic ulcers should not take betaine hy- drochloride. |
|
Purification Methods |
Recrystallise the salt from EtOH. Its solubility at 25o is 65% in H2O, and 5% in EtOH. [Edsall J Am Chem Soc 66 1767 1943, Kuhn & Ruelius Chem Ber 83 420 1950, Beilstein 4 III 1127, IV 2369.] |
|
Precautions |
People with a history of ulcers, heartburn, or other gastrointestinal symptoms should see a nutritionally oriented doctor before taking betaine hydrochloride, and no one should take more than 10 grains (650 mg) without a physician's recommendation. Large amounts of betaine hydrochloride can burn the lining of the stomach. If a burning sensation is experienced, betaine hydrochloride should be immediately discontinued. |
|
General Description |
Betaine?(trimethyl glycine) is an osmoprotectant, which is highly effective than proline. It is formed in from?choline. Betaine?is usually present in grains, spinach, beets,?broccoli, shellfish and marine algae. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H11NO2.ClH/c1-6(2,3)4-5(7)8;/h4H2,1-3H3;1H/p-1
Betaine hydrochloride synthetic method, ...
The invention discloses a method for pre...
The invention provides a compound contai...
Real-time monitoring of betaine aldehyde...
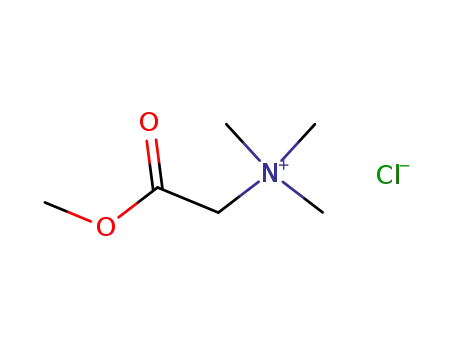
Trimethylammoniumessigsaeurebetain-methylester-chlorid

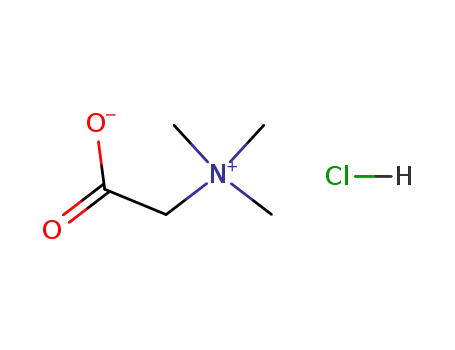
betaine hydrochloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water;
at 100 ℃;
for 5h;
Temperature;
Reagent/catalyst;
Molecular sieve;
|
98.6% |
N-<(ethoxycarbonyl)methyl>trimethylammonium chloride


betaine hydrochloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
water;
at 60 ℃;
for 5h;
Molecular sieve;
|
98.4% |
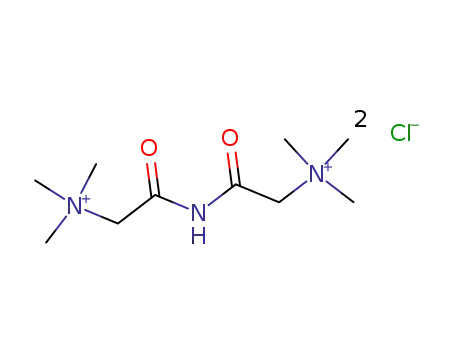
bis-(trimethylammonio-acetyl)-amine; dichloride
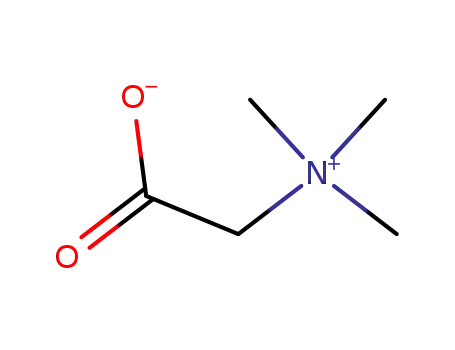
betaine
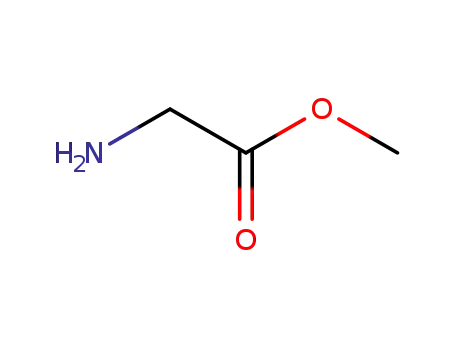
methoxycarbonylmethylamine
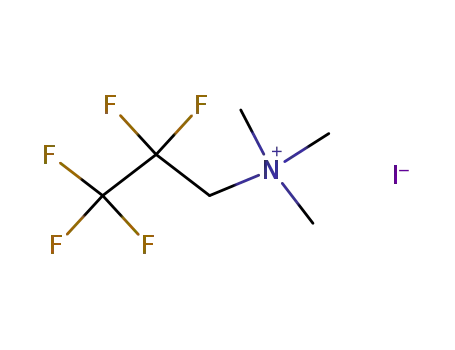
(2,2,3,3,3-Pentafluoropropyl)trimethylammonium iodide
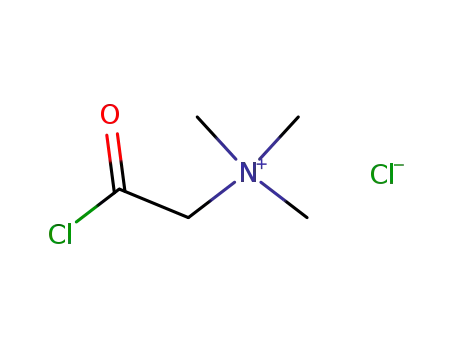
N-chlorobetainyl chloride
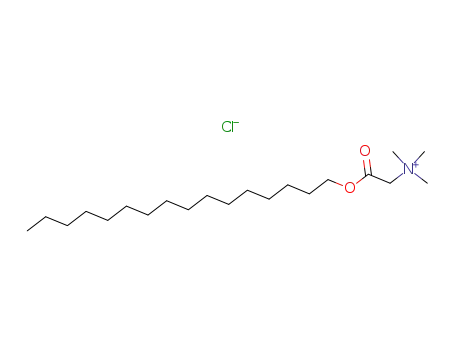
carbocetyloxymethyltrimethylammonium chloride
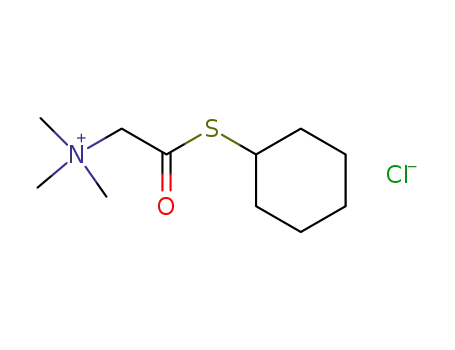
Cyclohexylsulfanylcarbonylmethyl-trimethyl-ammonium; chloride
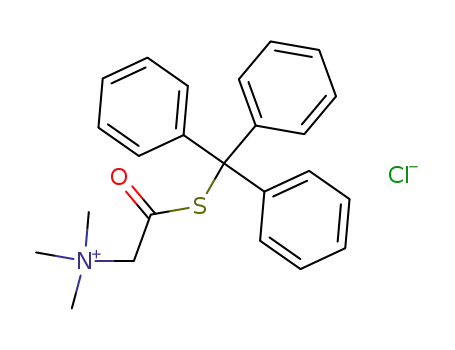
Chlorid des Thiobetain-S-triphenylmethylesters