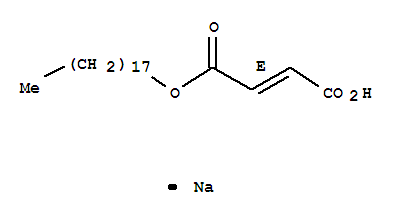

CasNo: 4070-80-8
MF: C22H39NaO4
|
Production Methods |
Stearyl alcohol is reacted with maleic anhydride. The product of this reaction then undergoes an isomerization step followed by salt formation to produce sodium stearyl fumarate. |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Sodium stearyl fumarate is used as a lubricant in capsule and tablet formulations at 0.5–2.0% w/w concentration. It is also used in certain food applications. |
|
Safety |
Sodium stearyl fumarate is used in oral pharmaceutical formulations and is generally regarded as a nontoxic and nonirritant material. Metabolic studies of sodium stearyl fumarate in the rat and dog indicated that approximately 80% was absorbed and 35% was rapidly metabolized. The fraction absorbed was hydrolyzed to stearyl alcohol and fumaric acid, with the stearyl alcohol further oxidized to stearic acid. In the dog, sodium stearyl fumarate that was not absorbed was excreted unchanged in the feces within 24 hours. Stearyl alcohol and stearic acid are naturally occurring constituents in various food products, while fumaric acid is a normal constituent of body tissue. Stearates and stearyl citrate have been reviewed by the WHO and an acceptable daily intake for stearyl citrate has been set at up to 50 mg/kg body-weight. The establishment of an acceptable daily intake for stearates and fumaric acid was thought unnecessary. Disodium fumarate has been reported to have a toxicity not greatly exceeding that of sodium chloride. |
|
storage |
At ambient temperature, sodium stearyl fumarate is stable for up to 3 years when stored in amber glass bottles with polyethylene screw caps. The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container in a cool, dry place. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Sodium stearyl fumarate is reported to be incompatible with chlorhexidine acetate. |
|
Regulatory Status |
GRAS listed. Permitted by the FDA for direct addition to food for human consumption as a conditioning or stabilizing agent in various bakery products, flour-thickened foods, dehydrated potatoes, and processed cereals up to 0.2–1.0% by weight of the food. Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral capsules and tablets). Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. |
InChI:InChI=1/C22H40O4.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-20-26-22(25)19-18-21(23)24;/h18-19H,2-17,20H2,1H3,(H,23,24);/q;+1/p-1/b19-18+;